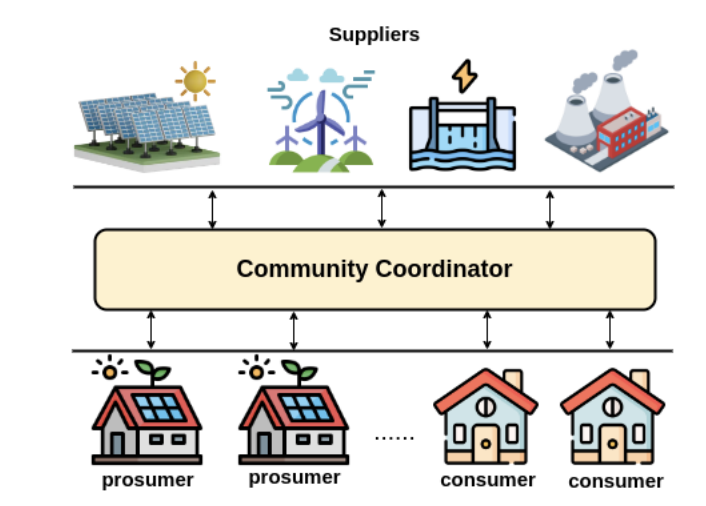
Traditional power grids generally carry power from a few central generators to a large number of users or customers. A Smart Grid represents a transformative evolution in the way electricity is generated, transmitted, distributed, and consumed. Unlike traditional power grids, a Smart Grid leverages cutting-edge technologies to enhance efficiency, reliability, and sustainability across the entire energy ecosystem. From these distributed energy resources emerged a new form of energy trading mechanism known as Peer-to-Peer (P2P) energy trading.
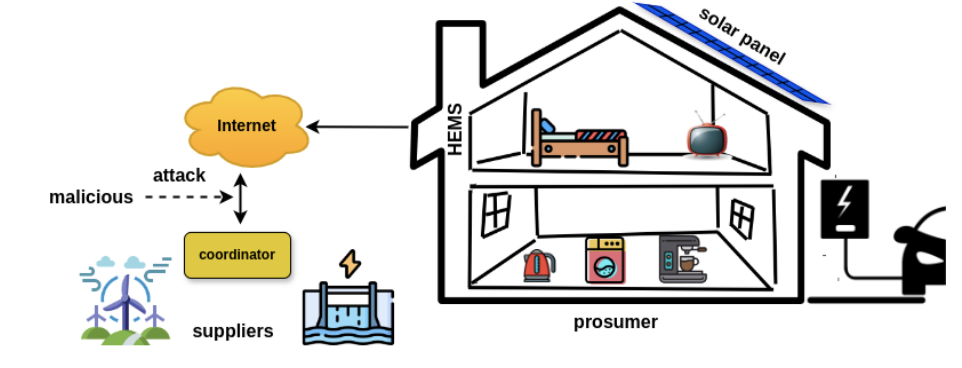
A solar-powered smart home equipped with Home Energy Management (HEM) regulates overall energy consumption. Smart plugs transmit their data to the HEM unit via a Zigbee network. The HEM unit shares household consumption data with other households (i.e., prosumers) and the coordinator. The attacker attempts to manipulate households’ consumption in two ways: an insider attack directed at the physical HEM host, and an outsider attack targeting the HEM through the network.
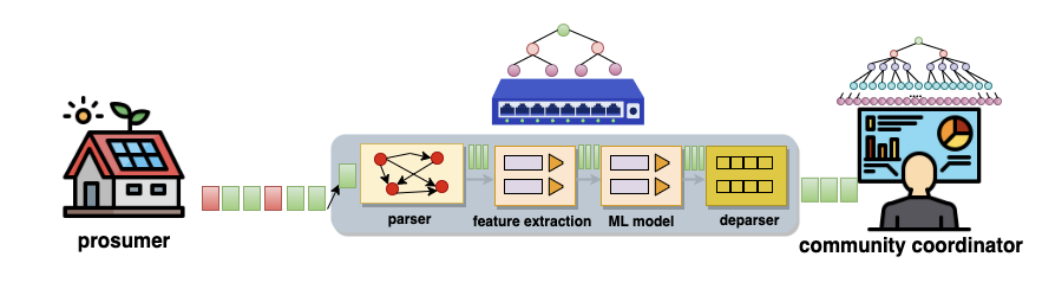
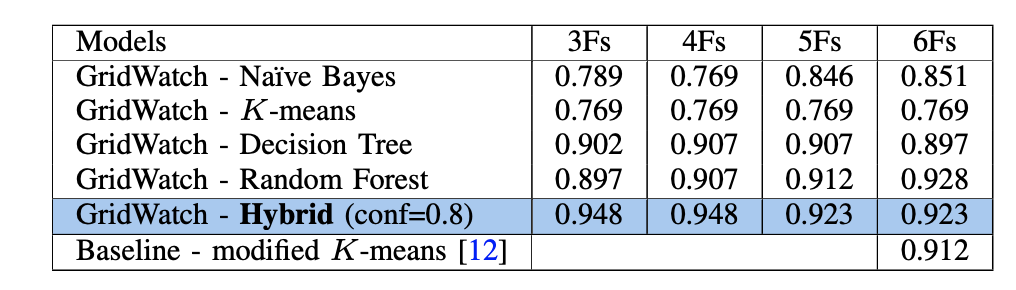
we introduce a novel architecture for realtime detection of FDIAs. Our solution, GridWatch, leverages in-network machine learning techniques to identify anomalies. GridWatch, implemented on a smart switch, enables the detection of malicious prosumers while data is being transmitted from the HEMs to the community coordinator. The architecture used by GridWatch builds upon the Protocol Independent Switch Architecture (PISA) of the smart switch. A small model is implemented in the network devices (i.e., smart switch) and a large model is implemented on the community coordinator server. First, the small model looks for the attack, and assigns a certain confidence level to classified traffic. If the classification of a packet has a confidence level below a configured threshold, the switch passes the packet to the server for further analysis by a large model. GridWatch is trained to differentiate attack events from normal ones with varying numbers of features, ranging from 3 to 6. GridWatch solution stands out as it requires no modifications on the prosumer’s end, including their HEM system. Furthermore, it does not require to have a full knowledge of the distributed network. Instead, the defensive strategy is integrated directly into the communication network, enabling real-time functionality and updates. Furthermore, this solution is power efficient.